A polygraph test, commonly known as a lie detector test, measures physiological responses to determine if a person is being deceptive. Here’s a detailed explanation you can use for your blog article:
Introduction to Polygraph Technology
Polygraph technology has been around since the early 20th century, evolving as a tool for detecting deception by analyzing various physiological indicators. It’s widely used in law enforcement, criminal investigations, and employment screenings, although its accuracy and ethical implications are often debated.
How Polygraph Tests Work
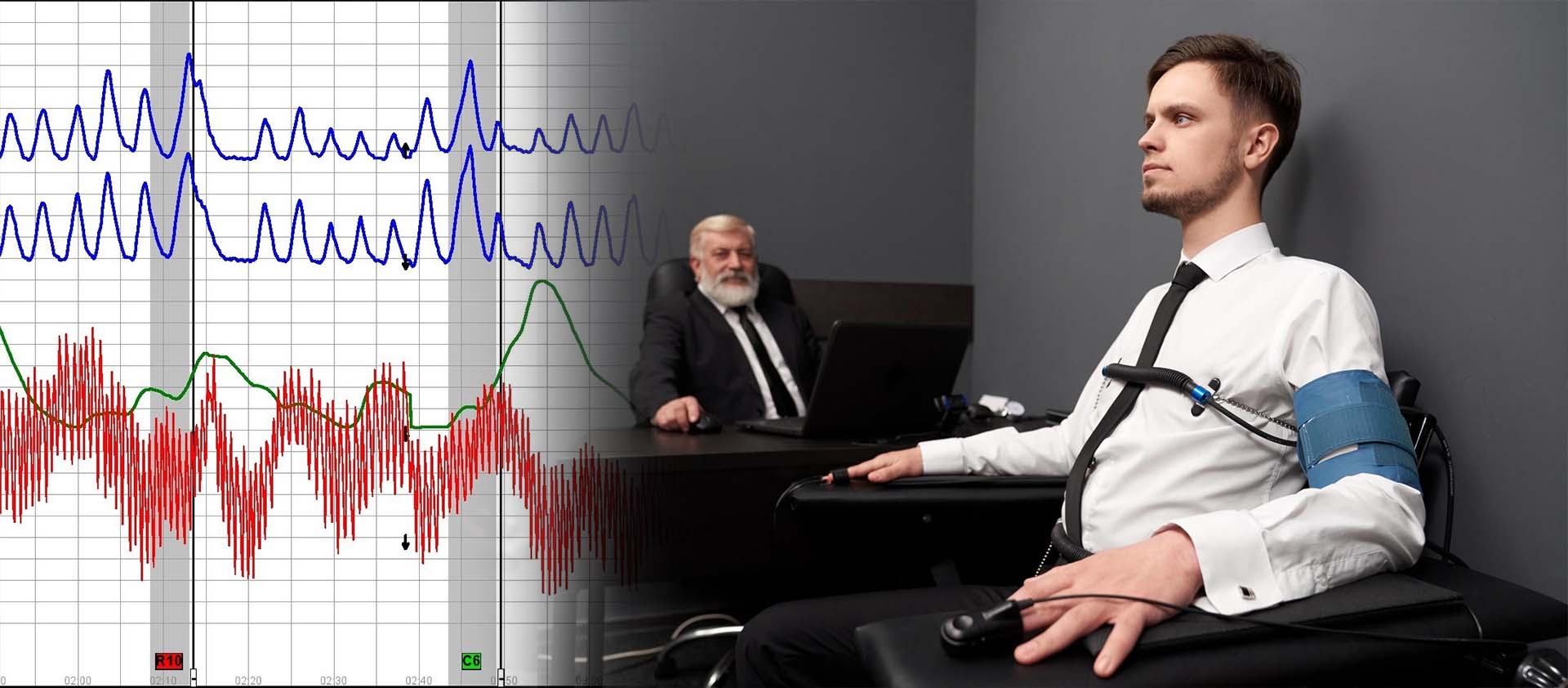
Polygraph tests are based on the premise that deceptive answers will produce physiological responses that can be measured. These responses are recorded through various sensors attached to the person being tested.
Physiological Indicators Measured:
- Heart Rate: The test monitors the heart rate, as an increase might indicate stress associated with lying.
- Blood Pressure: Changes in blood pressure can be a sign of nervousness, which could suggest dishonesty.
- Respiratory Rate: The test tracks breathing patterns, as irregularities may occur when a person is lying.
- Galvanic Skin Response (GSR): This measures the skin’s ability to conduct electricity, which can increase with sweating, a possible sign of stress or deception.
The Testing Process:
- Pre-Test Interview: The examiner explains the test and reviews the questions with the subject to establish baseline readings.
- Control and Relevant Questions: During the test, subjects answer control questions (which they’re likely to answer truthfully) and relevant questions related to the matter under investigation.
- Analysis: The examiner compares physiological responses to the control questions against responses to the relevant questions. Significant deviations may suggest deception.
Accuracy and Limitations
- Accuracy Debate: While proponents claim high accuracy rates (80-90%), critics argue that results can be influenced by anxiety, fear, or countermeasures, making them unreliable.
- False Positives/Negatives: A polygraph may falsely indicate deception (false positive) or fail to detect a lie (false negative). This has raised concerns about its fairness in legal and employment contexts.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Polygraph results are inadmissible in many courts due to questions about their reliability. Moreover, ethical concerns revolve around the potential for misuse and the stress it places on individuals.
Modern Advancements in Polygraph Technology
Recent developments aim to improve the accuracy and reliability of polygraph tests:
- Computerized Polygraphs: Modern polygraphs are now digital, allowing for more precise data collection and analysis.
- AI and Machine Learning: Researchers are exploring AI to analyze polygraph data, potentially reducing human error in interpreting results.
- Alternative Technologies: New technologies, like fMRI and voice stress analysis, are being studied as alternatives or supplements to traditional polygraph methods.
The accuracy of polygraph tests is a subject of ongoing debate. Proponents of polygraph technology claim that it can be highly accurate, with success rates often cited between 80% and 90%. However, these figures are contested by many experts who point out several factors that can influence the results:
Factors Affecting Polygraph Accuracy
Physiological Variability:
- Individual Differences: People React differently to stress, and not everyone experiences the same physiological changes when lying. Some individuals may naturally have heightened physiological responses, even when telling the truth, leading to false positives.
- Emotional State: Anxiety, fear, or nervousness unrelated to deception can also trigger physiological responses similar to those caused by lying, which can skew the results.
Test Administration:
- Examiner Skill: The accuracy of a polygraph test heavily depends on the skill and experience of the examiner. An experienced examiner is better at interpreting the data, but human error or bias can still affect outcomes.
- Question Formulation: The way questions are formulated and the context in which they are asked can impact the results. Poorly designed questions can lead to ambiguous responses, reducing the test's reliability.
Countermeasures:
- Intentional Manipulation: Some individuals may attempt to manipulate their physiological responses through countermeasures, such as controlled breathing, physical discomfort (like biting the tongue), or mental tricks. These techniques can sometimes reduce the accuracy of the test.
External Influences:
- Environmental Factors: External factors, such as room temperature, noise, or the subject's physical condition (e.g., fatigue, illness), can influence physiological responses and potentially affect the test's accuracy.
Scientific Consensus on Accuracy
The scientific community is divided on the reliability of polygraph tests. While some studies support high accuracy rates, others suggest that the margin of error is significant enough to question the test's validity in certain contexts, such as legal proceedings.
False Positives: A false positive occurs when the test indicates that a truthful person is lying. This can happen due to nervousness, misunderstanding of the questions, or other benign reasons.
False Negatives: A false negative happens when the test fails to detect deception. This might occur if the subject is particularly good at controlling their physiological responses or using countermeasures.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Due to these accuracy concerns, polygraph results are often inadmissible in court in many jurisdictions. The ethical implications of relying on a test with potential for error have led to strict guidelines on when and how polygraphs can be used, particularly in employment and criminal investigations.
Polygraph technology remains a controversial but widely used tool in detecting deception. While advancements are being made to enhance its accuracy, the debate over its reliability and ethical implications continues. Whether used in criminal investigations, employment screenings, or other fields, the polygraph test is a powerful tool that must be applied carefully and with a clear understanding of its limitations.














Comments & Discussion
Join the discussion by logging into your account.